Home » Power Electronics » Three- Phase Inverters
-
Three-Phase Inverters
Inverters are used to transform DC power into three-phase AC power. Todays inverters use high power switching transistors called IGBT's and/or MOSFETS. A single phase inverter consists of two switches, one from the positive DC rail tied to a common node and one from the negative DC rail tied to the common node. The AC power is extracted from the common node with respect to a center tapped ground between two capacitors. A good example of an inverter, though not a very efficient one, is an audio amplifier. The only modification to the amplifier is that the input to the amplifier need be a constant AC signal representing the desired output frequency.
A three-phase inverter is a combination of three single phase inverters along with synchronization so that the three phase voltages are separated by 120 degrees. Below is a schematic of the most simple three phase inverter topology. Another example of an inverter is given in the flywheel storage system link.
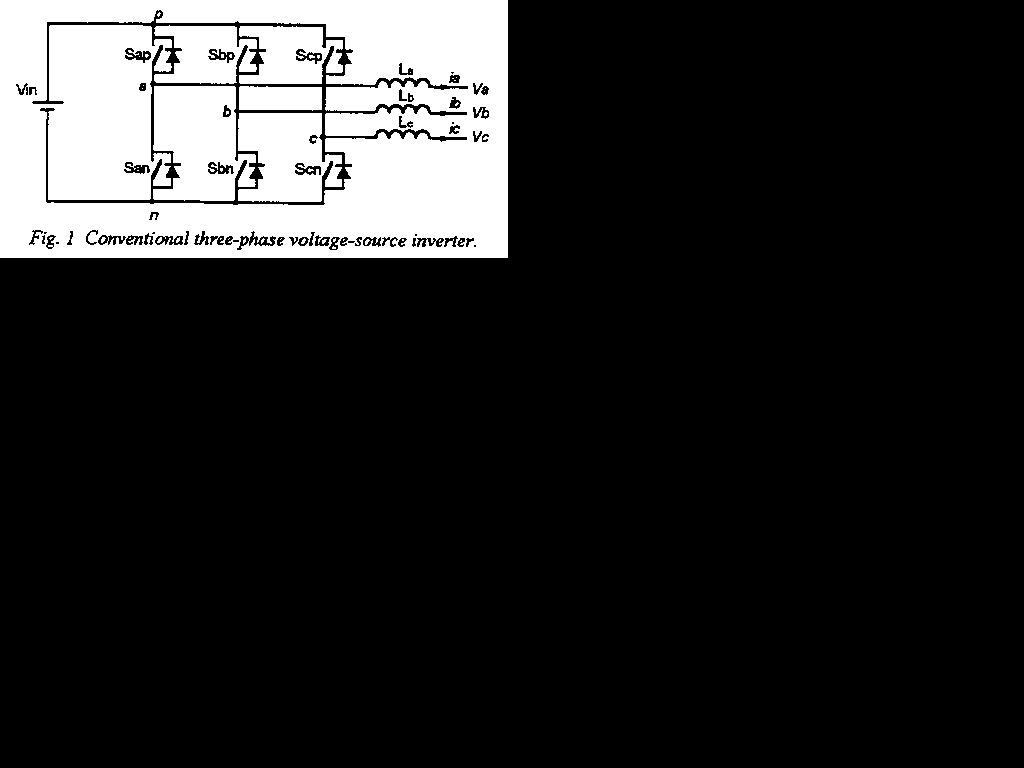
This schematic comes from the report: Three-Phase Soft-Switching Inverters for Electric Vehicle Applications which appeared in the 1995 VPEC seminar procedings. The authors are: S. Frame, S. Dubovsky, Q. Li, D. Katsis, C. Cuadros, D. Borojevic, and F.C. Lee.